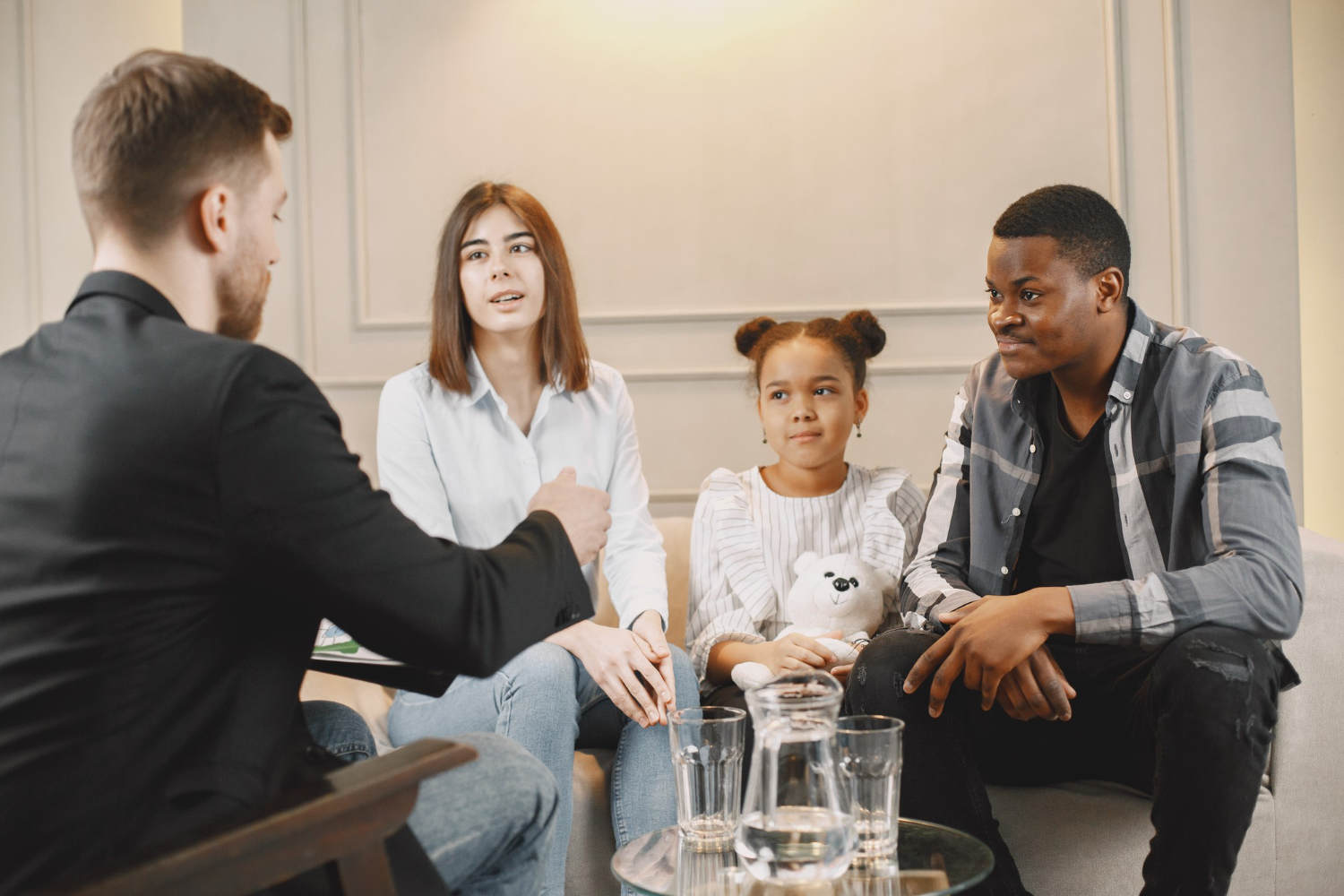
What is the Office of the Children’s Lawyer?
For those of you who are parents and are involved in Family Litigation in Ontario, you may have heard about the Office of the Children’s Lawyer (OCL). This brief blog will touch upon the basics points you need to know about this provincial government entity.
What is the OCL?
The Office of the Children’s Lawyer (OCL) operates as a specialized Ontario government agency, falling under the oversight of the Ministry of Attorney General. Established with a mandate to protect the rights of children under 18, the OCL plays a crucial role in ensuring their well-being and representation in legal matters.
What is the Role of the Office of Children’s Lawyer (OCL)?
In Ontario’s complex legal landscape, children involved in various disputes and proceedings often face challenges in having their voices heard and their interests prioritized. The OCL addresses this gap by offering impartial legal representation. This representation extends across a spectrum of cases, including contentious issues like custody battles, disputes over parental access, child protection hearings, and specific civil matters affecting minors. By serving as their legal voice, the OCL empowers children to participate meaningfully in legal processes that profoundly impact their lives.
Related:What All Divorcees Can Learn From a Couple That Spent 500K on a Child Custody Battle
Advocating for Children’s Voices
One of the OCL’s primary functions is to ensure that children’s perspectives are effectively communicated to the court. This involves more than mere representation; it encompasses a deep commitment to understanding each child’s unique circumstances, preferences, and concerns. Through skilled advocacy, the OCL endeavors to bridge the gap between legal proceedings and the lived experiences of children, thereby promoting fair and just outcomes.
Protecting Children’s Rights
Central to its mission, the OCL advocates fiercely for the protection of children’s rights throughout all stages of legal proceedings. This includes safeguarding their right to express their views freely and ensuring that those views are given due consideration by decision-makers. By actively involving children in decisions that affect them, the OCL helps to uphold their dignity and autonomy within the legal system.
Related: What is the Legal Age at Which a Child Can Decide Which Parent to Live With?
Support in Vulnerable Situations
Moreover, the OCL plays a pivotal role in cases where children may be vulnerable to neglect, abuse, or other forms of harm. In child protection matters, for instance, the agency’s intervention often becomes a lifeline, advocating for the safety and well-being of children who cannot advocate for themselves effectively. This proactive stance not only supports children during crises but also strives to prevent future harm through informed legal action and advocacy.
In essence, the Office of the Children’s Lawyer stands as a beacon of protection and advocacy within Ontario’s legal framework. By championing the rights of minors and ensuring their voices are heard, the OCL not only fulfills its statutory mandate but also embodies a commitment to justice and fairness for all children in the province.
Where Does the OCL Get its Power?
The Office of the Children’s Lawyer (OCL) derives its authority from specific legislation governing its operations within Ontario’s legal system. Key statutes that empower the OCL include the Children’s Law Reform Act (CLRA) and the Child, Youth and Family Services Act (CYFSA). These legislative frameworks define the scope of the OCL’s responsibilities and its role in safeguarding children’s rights and welfare across various legal contexts.
Additionally, provisions within the Family Law Act (FLA) and the Divorce Act (DA) outline circumstances where the OCL may intervene, particularly in disputes arising from family law matters. These statutes provide the foundational basis for the OCL’s involvement, ensuring that children’s interests are prioritized and protected in legal proceedings concerning custody, access, and other familial issues.
When Does the OCL Get Involved?
The OCL typically becomes involved in situations characterized by high conflict between parents or guardians, coupled with concerns regarding the child’s welfare. These concerns often encompass allegations of abuse, neglect, or instances where the child’s best interests may not be adequately addressed by the parties involved in the dispute.
In such scenarios, the OCL serves a crucial role in providing an impartial and independent assessment of the circumstances affecting the child. This assessment includes gathering relevant information, consulting with the child directly (if appropriate), and conducting thorough evaluations to understand the dynamics at play. Based on these findings, the OCL makes informed recommendations to the court regarding custody arrangements, parental access, and other pertinent matters that impact the child’s well-being.
By intervening in these complex and often sensitive situations, the OCL strives to ensure that the legal process remains child-centered and focused on promoting outcomes that align with the child’s safety, stability, and developmental needs. This proactive involvement underscores the OCL’s commitment to advocating for children’s rights and advocating for their interests within Ontario’s legal framework.
How Does the OCL Get Appointed?
The Office of the Children’s Lawyer (OCL) is appointed to represent the interests of children in various legal proceedings. Their involvement is crucial in ensuring that a child’s voice is heard and their rights are protected. There are several ways through which the OCL can be appointed:
- Typically by court order. Judges may request the OCL’s participation when they believe that a child’s interests need independent representation.
- Alternatively, by the parties’ request. The OCL can get involved upon the request of the parties to a legal dispute.
- Rarely, by the child him or herself. However, this does not arise often.
Who Acts on the OCL’s Behalf?
On behalf of children, the Office of the Children’s Lawyer (OCL) acts through appointed representatives. These individuals are typically lawyers, social workers, and other professionals who are trained to handle the complexities of representing children in legal matters.
Lawyers appointed by the OCL provide legal representation, advocating for the child’s best interests in court. Social workers, on the other hand, conduct thorough assessments of the child’s situation, considering factors such as home environment, relationships with family members, and any special needs the child may have. Together, these professionals collaborate to ensure that the child’s voice is heard and their rights are protected throughout the legal process.
What are the Powers of the OCL?
Primarily, the OCL represents children in litigation, acting as their voice in various legal proceedings. This representation includes conducting independent investigations to gather relevant information about the child’s circumstances.
The OCL’s representatives have the authority to interview family members, review documents, and consult with other professionals involved in the child’s life. Based on their findings, they make informed recommendations to the court regarding what they believe is in the child’s best interests.
These recommendations can influence decisions on matters such as custody, access, and child protection. Additionally, the OCL may provide reports and expert testimony to assist the court in understanding the child’s needs and perspectives. Through these powers, the OCL plays a vital role in ensuring that the child’s welfare is at the forefront of legal decisions.
In Family Disputes Between Parents, What Tasks is the OCL Responsible For?
In cases of family disputes between parents, the Office of the Children’s Lawyer (OCL) is tasked with several critical responsibilities to ensure the welfare of the child involved. The OCL’s involvement is designed to provide an objective assessment and make recommendations that serve the child’s best interests. These tasks include:
- Conducting thorough investigations, which may include interviews with the child, parents, and other relevant parties.
- Reviewing documents and other evidence to gather comprehensive information about the child’s situation.
- Making recommendations about living arrangements, access schedules, and other aspects of the child’s care and upbringing.
What Role Does the OCL Serve in Child Protection Cases?
In child protection cases, the Office of the Children’s Lawyer (OCL) plays a vital role in safeguarding the interests of children who are subject to protection applications. These cases often involve serious considerations about the child’s safety and long-term welfare. The OCL’s role in these cases includes:
- Representing children who are the subject of protection applications brought by child welfare agencies, and assisting the court on decisions about foster care, adoption, and termination of parental rights.
- Providing the court with a comprehensive understanding of the child’s situation through detailed reports and assessments.
- Advocating for outcomes that serve the child’s best interests, ensuring that the child’s needs and preferences are considered in legal decisions.
The Bottom Line
The OCL plays an indispensable role in the Ontario legal system. It steps into legal proceedings to safeguard the rights and interests of any children under 18 who are involved. By providing independent legal representation for these children, it helps ensure their voices are heard, and that their best interests are prioritized in decisions affecting their lives.